Understanding the SaaS Financial Model: Key Concepts and Methods

Most SaaS founders have a clear vision for their business. They are focused on creating new products, finding new markets, and attracting new customers. However, there may be a significant gap between the vision itself and the tangible data that will allow them to articulate where they are going—and convince investors of its viability.
At its most basic, a financial forecast model is a summary of your company’s financial position that helps forecast its future performance. This makes financial modeling an invaluable tool for any company, but it’s important to understand that it is built on numerous assumptions and inputs. Therefore, the model must reflect a holistic understanding of the industry and take its nuances into account. SaaS companies, for example, have unique expenses, such as hosting costs, and a business model based on recurring subscriptions rather than one-time purchases. As a result, they need specific financial models that accurately capture revenue, cost projections, customer metrics, and more.
Many founders do not prioritize financial modeling, doing it poorly or neglecting it altogether. Whether your goal is expansion, operational understanding and maintenance, or securing investments, a comprehensive financial model is invaluable. It provides the data necessary to make strategic decisions and comprehend how various factors will impact your business. Adopting a model tailored to your business’s requirements ensures that you and your team are well-prepared to make optimal decisions for your company. This includes effectively communicating future expectations to investors, managing the business, strategizing, and mitigating risks. Such practices position you for a robust exit strategy and a higher valuation.
In this blog, we will offer a high-level overview of a specific type of SaaS financial model that takes a top-down approach, helping you establish a solid foundation for cultivating effective financial modeling practices.
What is Financial Modeling for SaaS Companies?
Financial modeling is the creation of models to represent the potential performance of your company. There are several types of financial modeling, the most basic being the three-statement model, which links the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
In this post, we discuss the financial forecast model, which uses the past and current performance of a business to predict future results. It is the model we use most often when we work with clients.
The 3 Benefits of Preparing a Financial Model
There are a number of benefits to using an appropriate financial model, including the ability to identify risks, make more informed business decisions, and showcase your company’s potential to investors. The following aspects can be analyzed and corrected with the creation of a proper financial model:
1. Risk Mitigation
For SaaS companies, long-term stability relies on being able to predict challenges ahead of time. Using financial models that offer detailed revenue and expense projections, companies can identify potential threats and opportunities and better mitigate risks in both the present and the future.
2. Strategic Planning
Beyond offering predictions for the future, financial models also shed light on a company’s current financial health. These models act as a benchmarking tool, helping companies measure and compare key business metrics and allowing them to make decisions backed by data and projections.
3. Investor Relations
A clear, robust financial strategy is key to building trust with investors. Financial models offer a transparent view of a company’s current position and future potential, which in turn helps determine valuation and reassures investors that the company’s growth objectives align with their investment goals.
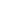
What are the Key Components of a SaaS Financial Model?
For SaaS businesses, understanding and predicting revenue is critical to sustainable growth. Financial modeling basics for SaaS companies include the following:
Revenue Forecasting
MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue): MRR is the predictable revenue that a SaaS company can anticipate on a monthly basis. This metric offers insight into the company’s short-term revenue prospects and can help in detecting trends or shifts in the revenue stream.
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue): The annualized version of MRR, ARR, is the amount of predictable revenue that a SaaS company can expect over a year, excluding any one-time payments or fees. Understanding ARR helps guide long-term planning and investment decisions, as it offers a broader view of the company’s revenue trajectory.
Churn Rate: Typically calculated monthly or annually, churn rate quantifies the percentage of customers who discontinue their subscription over a specified period. It’s an essential metric as it directly affects MRR and ARR. Monitoring and reducing churn is essential, as retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones.
Cost Projections
COGS: For SaaS companies, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the direct cost associated with delivering a software service to customers, including hosting costs, third-party service fees, and direct support costs. COGS helps determine gross margin, a primary indicator of a company’s profitability. COGS that are low relative to revenue indicate good operational efficiency and a scalable business model, so accurate forecasting is crucial for projecting profitability.
Operating Expenses: These are the costs incurred during the day-to-day operations of the business, such as salaries (except those included in COGS), sales & marketing, research & development, rent, utilities, and other general overhead costs. Operational expenses directly affect the operating margin and, therefore, the profitability of the company. Monitoring them is vital to ensuring that the business remains lean and efficient.
Customer Metrics
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC represents the average cost to acquire a single customer, taking into account new sales & marketing. A CAC that is high relative to customer LTV suggests inefficiencies in the marketing or sales processes, which could jeopardize profitability and future growth prospects. A CAC that is low relative to customer LTV, on the other hand, suggests an efficient acquisition process.
Retention Rate: Retention rate is the percentage of annual recurring revenue (ARR) a business retains over a specified period. Analyzing historical levels will help determine the best expectation for the business going forward while quantifying lost, gross, and net dollar retention will help you predict the spending levels of your existing customer base on a go-forward basis.
Lifetime Value (LTV): LTV is the total gross profit a business can expect from a single customer throughout their engagement. A high LTV suggests that the business is able to realize significant value from each customer and that customers find substantial value in the product, allowing for potentially higher investments in CAC. Comparing LTV to CAC can provide insights into the ROI of customer acquisition efforts. Ideally, the LTV should be significantly higher than the CAC for a SaaS business to be considered healthy. Understanding this metric helps leaders make decisions about what markets and how much to invest in acquiring and retaining customers.
Cash Flow Analysis: Cash flow is the amount of cash and cash equivalents that move in and out of your company. A cash flow analysis examines your income and expenses so you can understand how much working capital—money available for business operations—is available and determine how well you are managing expenses and obligations.
Break-Even Analysis: A break-even analysis predicts when the company will become profitable by calculating the number of sales needed to cover costs. The break-even point is achieved when total revenue equals total costs. This analysis gives you the minimum sales volume required to avoid losses and informs pricing, production, and sales strategies.
Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis evaluates the possible impact of different future events or circumstances on a specific outcome. Typically, it includes:
- A base scenario, which represents the most likely scenario given current conditions and known variables. This steady state assumes no major changes, either in control (for example, additional investments or cost cutting) or out of control (for example, market shifts or economic downturns) of the business.
- A conservative scenario, which uses more cautious assumptions, factoring in, for example, challenges or setbacks such as decreased demand, increased costs, or other unfavorable conditions.
- An aggressive scenario, which assumes favorable conditions such as rapid growth or increased market share that are likely to lead to a better-than-expected outcome.
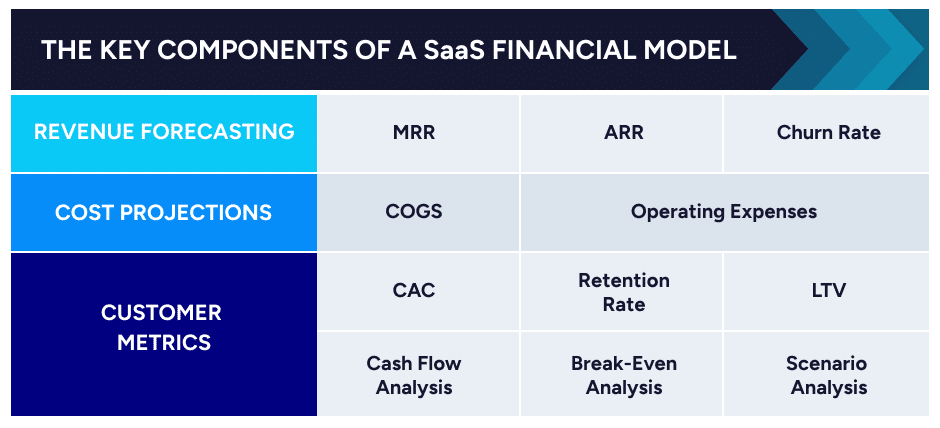
The following is an example of a financial model highlighting a conservative, realistic, and optimistic scenario.
4 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Preparing a Financial Model
To be effective, financial modeling must be accurate and reliable. Avoiding the following common mistakes will help you derive more value from your SaaS financial models and make more informed strategic decisions.
Mistake #1: Making overly optimistic projections without sufficient data
It’s not uncommon for models to display overly optimistic projections without solid data backing. To avoid this pitfall, try to create three versions of your financial model: aggressive, base, and conservative. This range of scenarios ensures you’re prepared for varying outcomes.
Mistake #2: Failing to account for additional resources to support expected growth
Companies often project aggressive growth without considering what the business needs to sustain said growth. For example, if you anticipate rapid customer acquisition, you must also anticipate a bigger customer support team is equipped to handle such a change. When setting growth targets, ensure that the relevant departments are scaled proportionately to accommodate and sustain that growth.
Mistake #3: Ignoring churn rate or underestimating its impact
The churn rate, or the percentage of customers who stop using your service over a certain period, plays a pivotal role in SaaS financial modeling. Ignoring or underestimating its impact can lead to skewed revenue predictions. It is essential to factor in realistic churn rates, using the company’s historical data as a baseline in conjunction with anecdotal reasons that it might be better or worse in the future to ensure accurate long-term projections.
READ MORE: Customer Churn Analysis: Why It’s Important for M&A
Mistake #4: Failing to make regular updates
A financial model isn’t a one-time creation; it is a dynamic tool that requires regular updates. It is crucial to update your model as new data becomes available. This ensures that your projections reflect actual business performance and that the model continues to serve as a reliable decision-making tool.
Tips for Creating an Effective SaaS Financial Model
Stay Flexible: The business environment, especially for SaaS companies, is dynamic. Your financial forecast model should be able to accommodate changes in market conditions, customer behavior, or internal business strategies. An inflexible model can quickly become obsolete, leading to misguided decisions.
Iterate Regularly: A SaaS financial model is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process, so update your model with new data and insights on a regular basis. Depending on the pace of change and the availability of fresh data, consider revising the model at least quarterly, if not monthly.
Collaborate: A comprehensive financial model requires input beyond just the finance team. Collaborate with various departments, from sales to customer support, to gather insights and make sure all relevant factors are considered. This collective approach ensures a more holistic and accurate representation of your business.
Seek Expertise: If there are areas of uncertainty or complexity in your model, talk to an expert. Financial consultants specializing in the SaaS industry can provide invaluable insights and best practices and help ensure that your model aligns with industry standards.
Dive into Your Company’s SaaS Financial Model
A well-crafted financial forecast model helps guide companies toward sustainable growth, informed decision-making, and, ultimately, an informed valuation. However, comprehensive financial modeling is complex, and even minor oversights can result in misleading or inaccurate projections.
If you are prepared to dive deeply into your business prior to considering a liquidation event, feel free to reach out to us for a complimentary, non-obligatory strategic assessment.